참고) STP 에 관련된 포스팅은 여러개로 이루어져 있으나 이 포스팅을 제외한 나머지는 수강생에만 유료강좌를 통해서 배포됩니다.
Network Redundancy
- 2024년에 변경된 CCNA Exam Blueprint에는 STP이 빠져있고, Rapid STP가 들어있다. 하지만 Rapid STP을 이해하기 위해서 선행적으로 Classic STP을 이해하여야 한다.
- Redundancy is an essential part of network design.
- Modern networks are expected to run 24/7/365. Even a short downtime can be disatrous for a business.
- If one network component fails, you must ensure that other components will take over with little or no downtime.
- As much as possible, you must implement redundancy at every possible point in the network.

- 위 토폴로지에서 PC는 일반적으로 하나의 네트워크 카드가 장착되어 있기 때문에, Access Switch의 이중화는 불가능하다. 하지만 중요한 역할을 하는 서버의 경우는 두개이상의 네트워크 카드가 장착되어 있기 때문에 Access 단에서 이중화가 가능하다(이는 CCNA 범위를 벗어나는 주제이다).
Loop 구조가있는 Switched Network의 문제

스위치로 구성된 네트워크에서 Loop 구조가 있으면 패킷의 무한루프가 발생한다. 3계층에서 발생하는 Loop는 IP 헤더의 TTL 필드로 인해서 어느 시점에 IP 패킷은 네트워크에서 사라지지만, 2계층 Loop에서 발생하는 이더넷 프레임은 영원히 살게된다. 이로 인해서 브로드캐스트 스톰(Broadcast Storm)이 발생한다.

2계층 루프 구조로 인해서 발생하는 문제는 Broadcast Storm 뿐만이 아니라 MAC Address Flapping도 있다. When frames with the same source MAC address repeatedly arrive on different interfaces, the switch is continuously updating the interface in its MAC address table.
Spanning Tree Protocol
- ‘Classic Spanning Tree Protocol’ is IEEE 802.1d.
- Switches from ALL vendors run STP by default.
- STP prevents Layer 2 loops by placing redundant ports in a blocking state, essentially disabling the interface.
- These interfaces act as backups that can enter a forwarding state if an active (=currently forwarding) interface fails.
- Interfaces in a forwarding state behave normally. They send and receive all normal traffic.
- Interfaces in a blocking state only send or receive STP messages (called BPDUs => Bridge Protocol Data Units).
스패닝트리 프로토콜 실습

- By selecting which ports are forwarding and which ports are blocking, STP creates a single path to/from each poitn in the network. This prevents Layer 2 Loops.
- There is a set process that STP uses to determine which ports should be forwarding and which should be blocking.
- STP-enabled switches send/receive Hello BPDUs out of all interfaces, the default timer is 2 seconds (the switch will send a Hello BPDU out of every interface, once every 2 seconds).
- If a switch receives a Hello BPDS on an interface, it knows that interface is connected to another switch (routers, PCs, etc. do not use STP, so they do not send Hello BPDUs).

- Switches use one field in the STP BPDU, the Bridge ID field, to elect a root bridge for the network.
- The switch with the lowest Bridge ID becomes the root bridge.
- ALL ports on the root bridge are put in a forwarding state, and other switches in the topology must have a path to reach the root bridge.

아래 토폴로지를 보고 루트 브리지를 결정하여 보자.
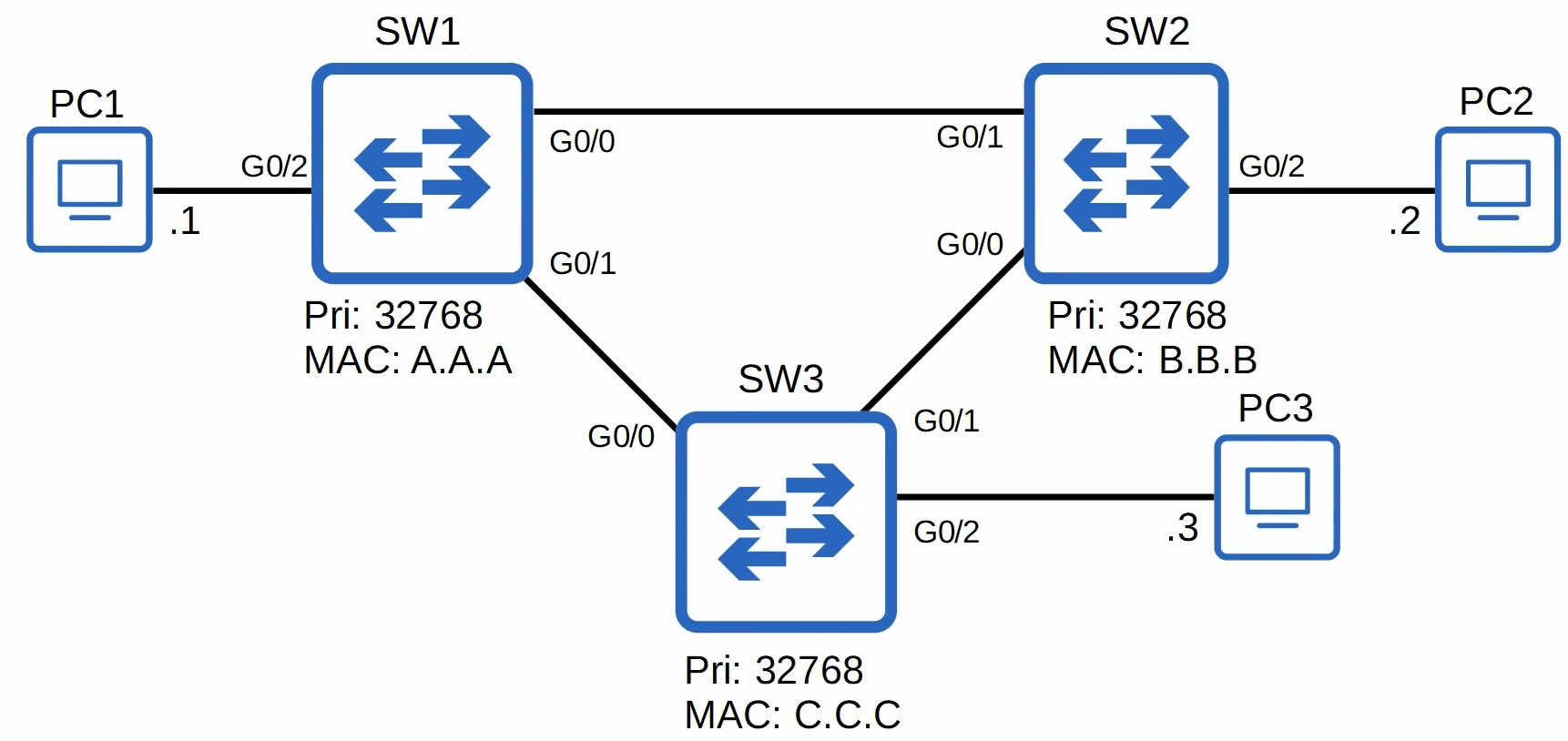
루트 브리지의 결정

브리지 ID의 결정원리

Cisco 스위치는 VLAN 마다 서로 다른 Spanning Tree Protocol을 운용하기 때문에, 하나의 인터페이스가 VLAN에 따라서 Forwarding 혹은 Blocking State에 서로 다른 상태로 있을 수 있다. 따라서 VLAN마다 상이한 STP이 돌기 때문에, VLAN 마다 Bridge ID도 서로 달라야 한다.


위 그림을 보면 알수 있겠지만 스위치의 Bridge Priority는 4096의 배수로 증가한다.



VLAN 1을 기준으로 하였을때 Bridge ID는 다음과 같다.


'Network > CCNA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| PortFast (1) | 2024.10.29 |
|---|---|
| STP (04) (0) | 2024.10.29 |
| 03장) 케이블, 커넥터 그리고 포트 (0) | 2024.07.24 |
| (02장) Network devices (0) | 2024.07.24 |
| 7 IPv4 Addressing (0) | 2024.06.05 |



